Understanding Wood Glue

Wood glue might seem like a simple supply on your workbench, but using the right kind can make or break your project—literally. Whether you’re repairing a chair, crafting a cutting board, or building outdoor furniture, knowing your glue types and how to use them properly will lead to stronger joints, cleaner results, and longer-lasting projects. Let’s break down the most common types of wood glue, what makes them different, and when to use each one.
Gorilla Glue vs Titebond Glue
Gorilla Glue and Titebond Glue are both strong adhesives, but they serve different purposes. Gorilla Wood Glue is a polyurethane adhesive known for bonding a wide range of materials—including wood, metal, stone, and plastic—and it’s fully waterproof, making it ideal for outdoor projects or when gluing dissimilar materials. It expands as it cures, which helps fill gaps but can also be messy.
Titebond, on the other hand, is a wood glue (PVA-based) specifically designed for wood-to-wood joints. It's easy to clean up with water, doesn’t expand, and comes in several formulations like Titebond II and Titebond III for water resistance and extended open time. For clean, tight wood joints—especially in furniture or cabinetry — Titebond is the go-to choice. Use Gorilla Glue when you're working with mixed materials, uneven surfaces, or need a truly waterproof bond.
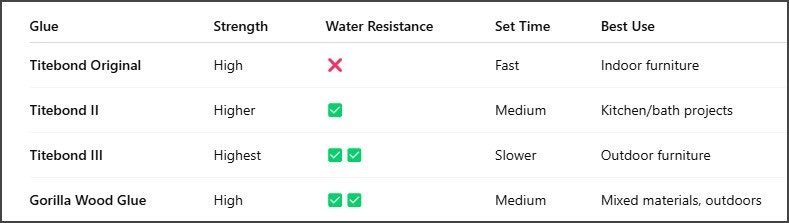
Other Types of Wood Glue and Their Applications
Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA) - These are the most prevalent wood glues, suitable for indoor applications. They dry clear, are easy to clean with water, and are non-toxic. Examples include Titebond Original and Elmer's Carpenter's Wood Glue.
Aliphatic Resin (Yellow Glue) - Similar to PVA but with added heat and water resistance, aliphatic resin glues are favored for their quick setting time and strong initial tack. They're excellent for woodworking joints that require precise alignment.
Epoxy - A two-part adhesive known for its exceptional strength and gap-filling properties. Epoxy is suitable for bonding dissimilar materials and is often used in situations where maximum durability is required.
Polyurethane Glue - This glue expands as it cures, making it effective for bonding uneven surfaces. It's waterproof and suitable for outdoor projects, but the foaming action requires careful application to prevent mess.
Cyanoacrylate (CA) Glue - Also known as super glue, CA glue is perfect for quick repairs and small joints. It bonds rapidly but is brittle, so it's not recommended for load-bearing joints.
Hide Glue - Traditional animal-based glue that's still used in fine woodworking and instrument making due to its reversibility and strong bond. Liquid hide glue offers a longer open time, making it more user-friendly.
What Wood Glue Is Best
James Wright of Wood By Wright on YouTube recently conducted a massive test of common wood glue. 32 types of glue were pitted against each other to find out which was the best choice for one of four different situations: long grain to long grain, long grain to end grain, gap-filling, and exterior conditions. The answer may be different than you think. Check out the spreadsheet of compiled test results or watch the video below.
Keep the inspiration coming!
Subscribe to our newsletter for more woodworking tips and tricks




